Let’s assume that at the end of a period, we have 1000 units of raw materials left. Of those 1000 units, 600 were purchased at one price, and 400 were purchased earlier at a different price, as shown below. To calculate ending Inventory cost using the property plant and equipment ppande definition method can take a lot of work, and may require us to create a running tabular balance to keep track of how much we paid for each item. Kristin is a Certified Public Accountant with 15 years of experience working with small business owners in all aspects of business building.
Periodic Inventory System:
The weighted average method weighs the average cost of Inventory, over the period. Depending on our Inventory system, we can use either Weighted Average Periodic or Weighted Average Perpetual. That would leave 50 units from beginning inventory and 75 from the purchase on January 3rd. Update the list of goods available for sale to reflect what was sold and the additional purchase on January 12. While this check figure will not ensure that you picked the right units, it will ensure that you accounted for all the units and calculated the cost correctly. Calculate the value of Bill’s ending inventory on 4 January and the gross profit he earned on the first four days of business using the FIFO method.
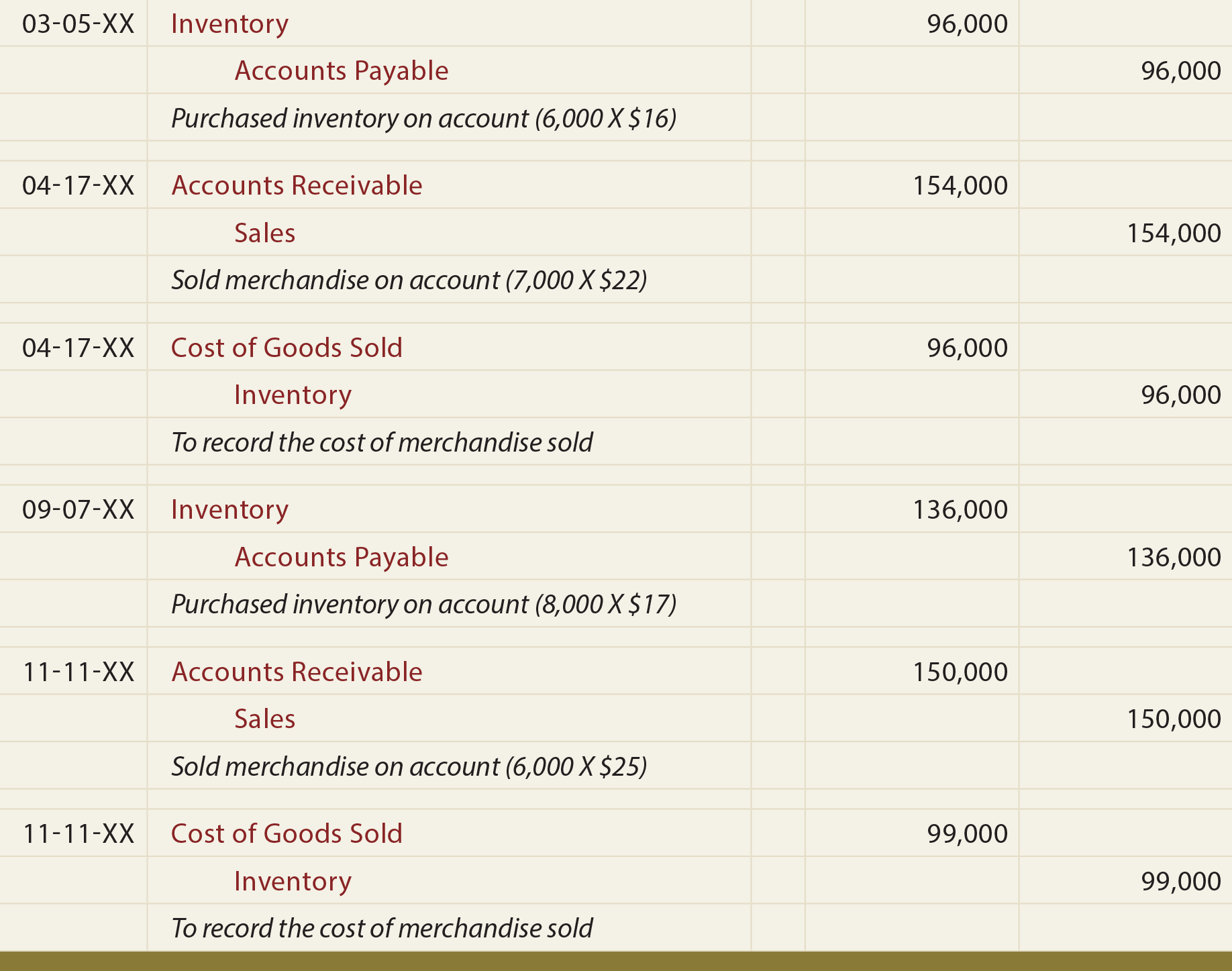
Perpetual vs. Periodic Inventory Systems
So, the company’s management is responsible for determining the best cost flow assumption. The assumption is certainly a subjective matter, and the definition of “best” will depend on the business type. The preceding illustrations were based on the periodic inventory system.
Inventory and Cost of Goods Sold Outline
- The accounting period can be in months, quarters or a calendar year.
- The inventory item sold is assessed a higher cost of goods sold under LIFO during periods of increasing prices.
- For instance, real-time inventory information is vital for the financial and accounting teams.
At any point in time, the perpetual inventory card can, therefore, provide information about purchases, cost of sales and the balance in inventory to date. Journal entries are not shown, but the following discussionprovides the information that would be used in recording thenecessary journal entries. Each time a product is sold, a revenueentry would be made to record the sales revenue and thecorresponding accounts receivable or cash from the sale.
If accounting for sales and purchase is kept separate from accounting for inventory, the measurement of inventory need only be calculated once at the period end. This is a more practical and efficient approach to the accounting for inventory which is why it is the most common approach adopted. Perpetual FIFO is a cost flow tracking system under which the first unit of inventory acquired is presumed to be the first unit consumed or sold.
Ending inventory was made up of 30 units at $21 each, 45units at $27 each, and 210 units at $33 each, for a total LIFOperpetual ending inventory value of $8,775. Once those units were sold,there remained 30 more units of beginning inventory. At the time of the secondsale of 180 units, the FIFO assumption directs the company to costout the last 30 units of the beginning inventory, plus 150 of theunits that had been purchased for $27. Thus, after two sales, thereremained 75 units of inventory that had cost the company $27 each.The last transaction was an additional purchase of 210 units for$33 per unit. Ending inventory was made up of 75 units at $27 each,and 210 units at $33 each, for a total FIFO perpetual endinginventory value of $8,955. The three cost flow assumptions that businesses use for this are FIFO, LIFO, and the Weighted Average Cost (WAC).

The alternate method of LIFO allows companies to list their most recent costs first in jurisdictions that allow it. FIFO assumes that assets with the oldest costs are included in the income statement’s Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The remaining inventory assets are matched to assets that were most recently purchased or produced. So, after the sale on January 15, the business records COGS of $98 and has $42 worth of inventory remaining, according to the perpetual FIFO method. The inventory record and COGS are updated immediately after the sale, which is the “perpetual” part of the perpetual FIFO method.
This approach reflects the natural flow of inventory for many types of businesses, especially those dealing with perishable goods. Moreover, during periods of inflation, using FIFO results in a lower COGS and higher inventory value, which leads to higher net income and taxes compared to other methods like LIFO (Last In, First Out). On the other hand, weighted average perpetual constantly updates the weighted average cost. To determine the cost of ending Inventory using the Weighted Average Perpetual method will likely require us to create a table so that we can keep track of the continuously changing cost.
While there is a constant, automatic product tracking system, there are still ways to lose positive inventory control. Statements are more transparent and it’s more difficult to manipulate FIFO-based accounts to embellish the company’s financials. FIFO is required under the International Financial Reporting Standards and it’s also standard in many other jurisdictions. The Statement of Financial Position (a.k.a Balance Sheet using Canadian ASPE accounting standards) presents the company’s total assets,…
